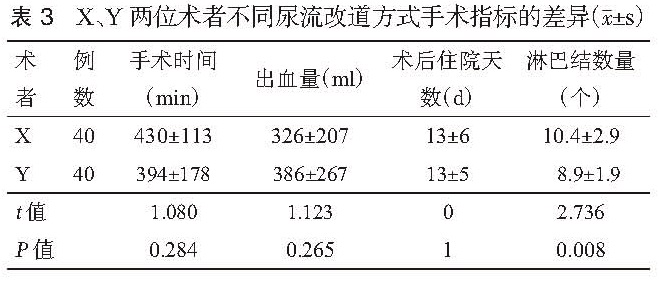
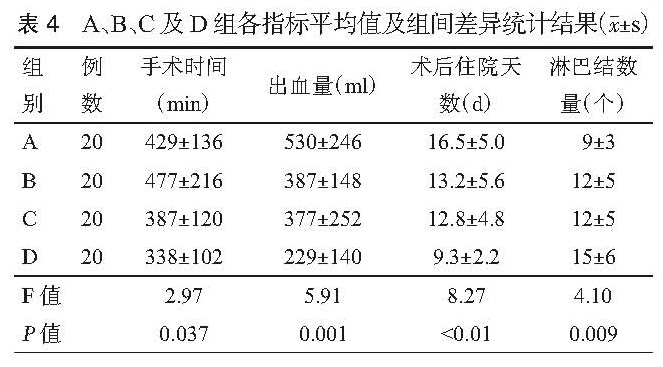
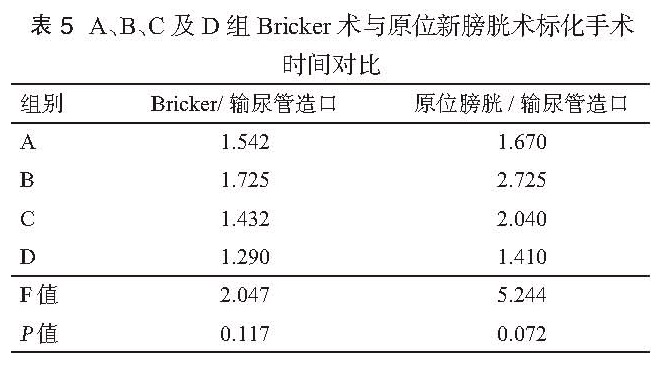
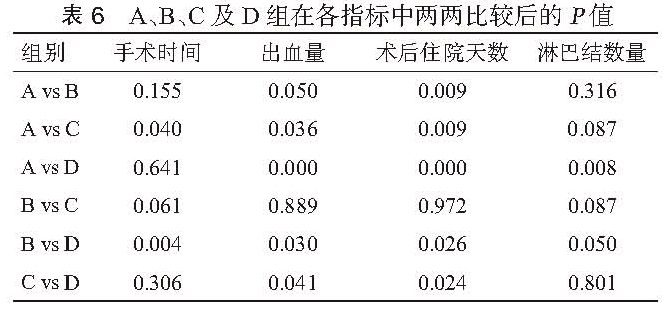
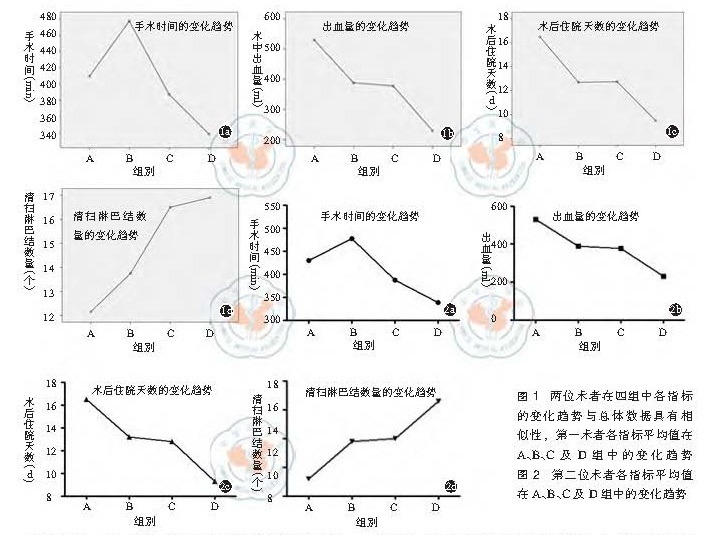
目的 探讨腹腔镜下根治性膀胱切除术( LRC)的学习曲线。方法 回顾性统计分析 2011年 1月至 2015年 12月于第二军医大学附属长海医院行 LRC的患者共 80例,其中男性 70例,女性 10例,年龄范围 27~84岁,中位年龄 63.5岁,既往腹部手术史 11例。病理分期: <T2期 32例, T2期 27例,T3期 15例,T4期 6例。其中输尿管皮肤造口 19例,Bricker术 53例,原位新膀胱术 8例。按照手术时间先后顺序,分成 A(第 1~20例),B(第 21~40例),C(第 31~60例),D(第 61~80例)四组。四组患者在性别构成、年龄、腹部手术史、尿流改道方式及肿瘤分期上差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05),比较各组手术时间、术中出血量、术后住院天数、清扫淋巴结数量等指标,并观察各指标的变化趋势。结果 手术均顺利完成,无中转开放。四组患者在手术时间、术中出血量、术后住院天数及清扫淋巴结数量上差异均具有统计学意义( P<0.05)。各组手术切缘均为阴性,并发症发生率的差别无统计学意义(P>0.05)。进一步两两比较结果显示,A组与 B组比较,手术时间、清扫淋巴结数量上的差异无统计学意义( P<0.05),但在术中出血量、术后住院天数上的差异均具有统计学意义( P<0.05)。B组与 C组仅在手术时间、清扫淋巴结数量上差异具有统计学意义( P<0.05),B组和 D组比较,四类指标之间的差异均具有统计学意义( P>0.05)。C组与 D组比较,手术时间及清扫淋巴结数量上无统计学差异( P>0. 05),而在出血量和术后住院天数上的差异具有统计学意义( P<0.05)。手术时间、术中出血量及术后住院天数随着手术例数的增加而逐渐下降,清扫淋巴结的数量则不断上升。结论 LRC具有明显的学习曲线,单个术者约行 30例 LRC手术后,手术时间及清扫淋巴结数量的学习曲线方能趋于稳定状态。而术中出血量及术后住院天数随着手术例数的不断增加呈阶梯状下降, 40例 LRC手术后降至最低水平,术者操作的熟练程度能够得到进一步的提升。
Objective To explore the learning curve for laparoscopic radical cystectomy. Methods From January 2011 to December 2015, clinical data of 80 cases (70 male and 10 female) underwent laparoscopic radical cystectomy(LRC) in our hospital, which were performed by two experienced urological experts were analyzed retrospectively. The median age was 63.5 years (27 to 82 years). 11 cases had history of abdominal surgery. Pathological stage: 32 cases of them had <T2 disease, 27 cases had T2 disease, 15 cases had T3 disease, 6 cases had T4 disease. Double cutaneous ureterostomy, bricker operation and ideal neobladder were conducted in 19, 53 and 8 cases, respectively. According to the surgical sequence, the 80 cases were divided into four groups, including Group A (1th to 20th ), Group B (21th to 40th), Group C (41th to 60th) and Group D (61th and 80th). The constituent of gender, age, history of abdominal surgery, the type of urinary diversion and tumor stage among four groups had no significant difference (P>0.05). The operating time, the blood loss, postoperative hospital stay and the total retrieved lymph nodes among the four groups were compared, the variational tendency about them was observed. Results All operations were completed smoothly, and hadn't been transferred to open. The differences in operating time, blood loss, postoperative hospital stay and the amount of lymph nodes dissected among the four groups were statistically significant (P<0.05). Nonetheless, the differences in incidence of complications and blood transfusion rate had no statistical significance (P>0.05). None of the surgical margins was positive. Further, betweet group A and group B, the operating time and the amount of lymph nodes dissected had no statistical significance (P<0.05), but in intraoperative blood loss and postoperative hospital stay, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). When group B compared with group C, the differences in operating time and the amount of lymph nodes dissected were statistically significant (P<0.05), when compared with group D, the differences about the four indexes were statistically significant (P<0.05). Eventually, the operating time and the amount of lymph nodes dissected between group C and group D had no (P>0.05), however, differences of blood loss and postoperative hospital stay had statistical significance (P<0.05). Conclusion When individual surgeon experienced 30 cases LRC, his operating time and the amount of lymph nodes dissected would lean to be stable and along with the increasing accumulation of surgical volume amount, after 40 cases LRC, the intraoperative blood loss and postoperative hospital stay which declined with the mode of ladder, would drop to the lowest level.