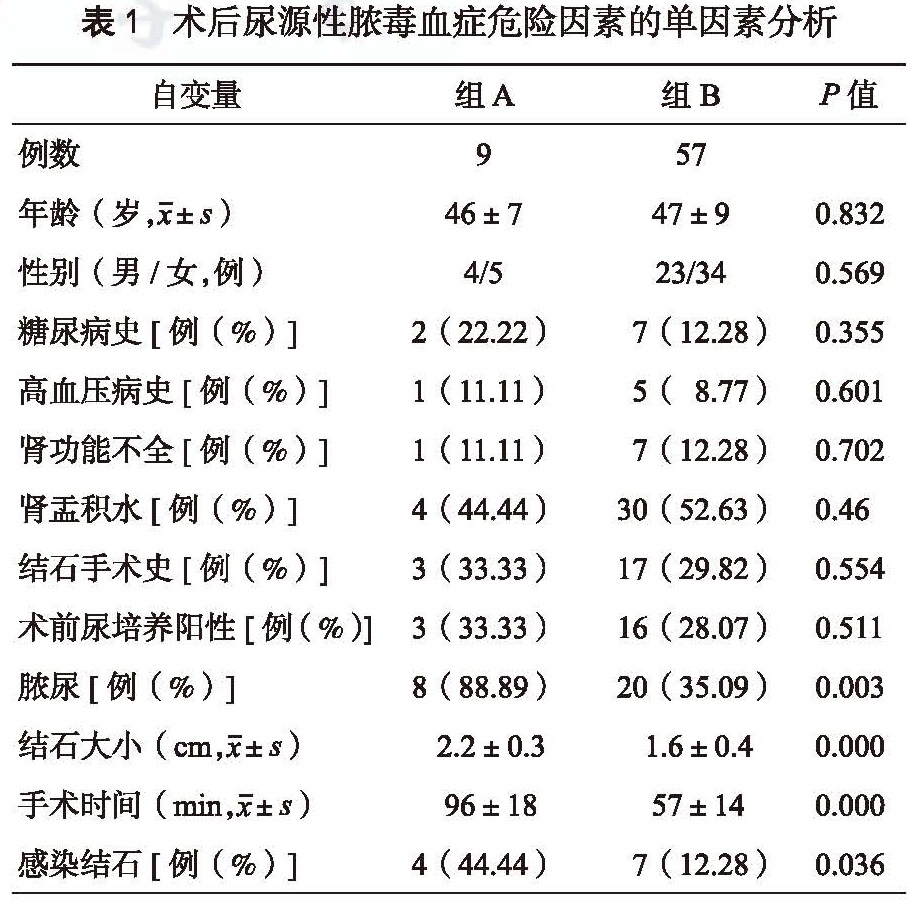
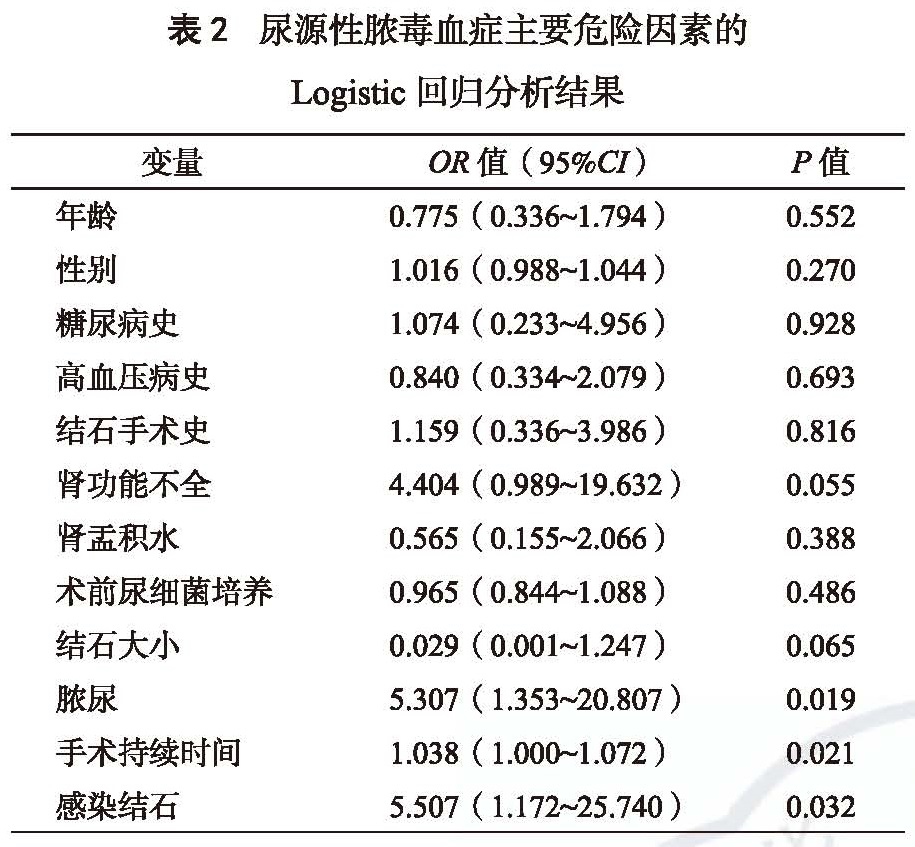
目的 探讨输尿管软镜联合钬激光治疗肾结石术后发生尿脓毒血的危险因素。方法 回顾性分析南方医科大学附属江门医院自2015 年1 月至2016 年9 月期间66 例输尿管软镜术后患者的临床资料。对患者的一般资料进行收集整理,统计分析输尿管软镜术后尿脓毒血症的危险因素。结果 66 例肾结石患者均顺利完成输尿管软镜联合钬激光碎石手术,术后9 例(13.6%)患者发生尿脓毒血症。术后尿脓毒血症危险因素的单因素分析中,脓尿、结石大小、手术持续时间、感染性结石有统计学意义(P<0.05)。在对包括年龄、性别、糖尿病史、高血压病史、结石手术史、肾功能不全、肾盂积水、术前尿细菌培养、结石大小、脓尿、手术持续时间、感染性结石等作为自变量的多因素Logistic回归分析中,术后尿脓毒血症的危险因素有脓尿(P=0.019),手术持续时间(P=0.021),感染性结石(P=0.032)。结论 脓尿、手术持续时间、感染性结石是输尿管软镜碎石术后尿脓毒血症的危险因素。
Objective To evaluate the effectiveness of flexible ureteroscopy (FURS) for treating kidney stones and the risk factors of urosepsis following flexible ureteroscope with holmium laser. Methods The data of 66 patients with kidney stones who underwent flexible ureteroscopy with holmium laser at our hospital from January 2015 to September 2016, including gender, age, comorbidity, urine analysis results, urine culture results, blood test results, stone size, and operative duration were analyzed retrospectively. Patients with and without urosepsis were assigned to groups A and B, respectively. The dependent variables were postoperative urosepsis, and the risk factors for urosepsis following flexible ureteroscope were assessed using Chi-square tests and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Results All surgeries were successfully completed. The incidence of urosepsis after FURS was 13.6% (n=9). Univariate analyses of groups A and B indicated that pyuria, stonesize, operative duration, and infectious stones were significantly different between two groups (P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analyses indicated that pyuria (P=0.019), operative duration (P=0.021), and infectious stones (P=0.032) were independently related to urosepsis. Conclusion Pyuria, operative duration, and infectious stones were risk factors for urosepsis following flexible ureteroscopy.