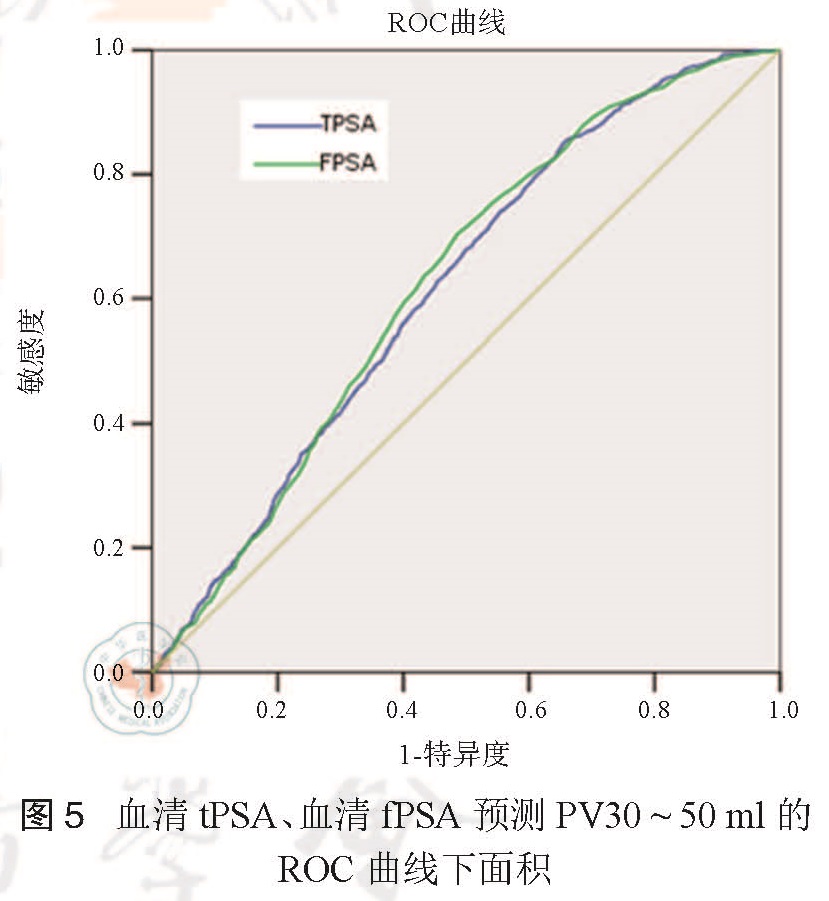
目的 通过比较血清总前列腺特异性抗原(tPSA)、游离前列腺特异性抗原(fPSA)与年龄预测前列腺体积(PV)大小的准确性,寻找预测 PV简便易行、较准确的预测因子。方法 收集 2005年 1月至 2014年 12月因下尿路症状到我院诊治下尿路症状 /良性前列腺梗阻(LUTS/BPO)患者的年龄、PV及 PSA检测值;采用 SPSS13.0软件处理数据,用皮尔森线性相关关系描述年龄、血清 tPSA及血清 fPSA与 PV的相关性,并采用卡方检验及受试者特征曲线(ROC)分析比较血清tPSA、血清 fPSA预测 PV的准确性。结果 入选 6308例男性,皮尔森线性相关分析显示年龄-PV、tPSA-PV和 fPSA-PV的相关系数分别是0.197、0.434、和0.446,其 P值均<0.05,具有相关性;在 tPSA为0~4 μg/L时,tPSA和 fPSA预测 PV在(30~50)ml、(50~70)ml和 PV>70 ml组的 AUC-ROC分别为(0.617、0.732、0.761)和(0.625、0.738、0.767);在 tPSA为 0~4 μg/L时, tPSA和 fPSA预测 PV在(30~50) ml、(50~70)ml和 PV>70 ml组的最佳临界值分别为 tPSA(1.3 μg/L、 1.6 μg/L、2.0 μg/L)和 fPSA(0.3 μg/L、0.4 μg/L、0.5 μg/L)。结论 中国 LUTS/BPO男性血清 fPSA与 PV正相关程度最高,血清 tPSA与 fPSA均可作为独立预测因子预测中国 LUTS/BPO男性的 PV,可作为临床上预测 PV简便易行的指标,其中 fPSA预测的准确性更高。
Objective To compare the accuracy of serum total prostate-specific antigen (tPSA), free PSA (fPSA) and age in predicting prostate volume (PV), aiming to identify the simple and accurate biomarkers for predicting PV. Methods Age, PV, and PSA values of patients diagnosed with lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic obstruction (LUTS/BPO) admitted to our hospital from January 2005 to December 2014 were collected. The data was processed using SPSS 13.0 statistical software. Pearson's linear correlation was utilized to describe the correlation between age, serum tPSA, serum fPSA and PV. Chi-square test and the receiver characteristic curve (ROC) were used to analyze and compare the accuracy of serum tPSAand fPSAin predicting PV. Results Atotal of 6308 male patients were enrolled. Pearson's linear correlation analysis demonstrated that the correlation coefficients of age-PV, tPSA-PV and fPSA-PV were 0.197, 0.434, and 0.446, respectively (all P<0.05). When tPSA was 0-4 μg/L, the AUC-ROC of tPSA and fPSA in predicting PV in the (30-50), (50-70) and >70 ml groups were (0.617, 0.732, 0.761) and (0.625, 0.738, 0.767), respectively. When tPSA was 0-4 μg/L, the optimal cut-off values of tPSA and fPSA in predicting PV in the (30-50), (50-70), and PV> 70 ml groups were (1.3 μg/L, 1.6 μg/L, 2.0 μg/L) and (0.3 μg/L, 0.4 μg/L, 0.5 μg/L), respectively. Conclusion s The serum fPSA possesses the highest positive correlation with PV in the male LUTS/BPO patients in China. Serum tPSA and fPSA can be considered as independent biomarkers to predict the PV in this population, which can be used as simple and convenient predictors for PV in clinical practice. fPSA yields higher prediction accuracy compared with tPSA.